Data Management (2025 updated for metacat/justIN/rucio)
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 15 minQuestions
What are the data management tools and software for DUNE?
Objectives
Learn how to access data from DUNE Data Catalog.
Learn a bit about the justIN workflow system for submitting batch jobs.
Table of Contents for 03-data-management
- Session Video - Live Notes
- Introduction
- How to find and access official data
- Official datasets
- What is metacat?
- Find a file in metacat
- Example of doing a metacat search
- then do queries to find particular groups of files
- What do those fields mean?
- find out how much raw data there is in a run using the summary option
- Fast web catalog queries
- Command line tools and advanced queries
- metacat web interface
- Example of finding reconstructed Monte Carlo
- you can use the web data catalog to do advanced searches
- get a limited number of files in a query
- find out how much data there is in a dataset
- What describes a dataset?
- What files are in that dataset and how do I use them?
- Finding those files on disk
- Getting file locations using Rucio
- More finding files by characteristics using metacat
- Accessing data for use in your analysis
- Quiz
- Useful links to bookmark
Session Video
The session video on December 10, 2024 was captured for your asynchronous review.
Introduction
What we need to do to produce accurate physics results
DUNE has a lot of data which is processed through a complicated chain of steps. We try to abide by FAIR (Findable, Accesible, Intepretable and Reproducible) principles in our use of data.
Our DUNE Physics Analysis Review Procedures state that:
-
Software must be documented, and committed to a repository accessible to the collaboration.
The preferred location is any repository managed within the official DUNE GitHub page: https://github.com/DUNE.
There should be sufficient instructions on how to reproduce the results included with the software. In particular, a good goal is that the working group conveners are able to remake plots, in case cosmetic changes need to be made. Software repositories should adhere to licensing and copyright guidelines detailed in DocDB-27141.
-
Data and simulation samples must come from well-documented, reproducible production campaigns. For most analyses, input samples should be official, catalogued DUNE productions.
How we do it ?
DUNE offical data samples are produced using released code, cataloged with metadata that describes the processing chain and stored so that they are accessible to collaborators.
DUNE data is stored around the world and you cannot directly log into most of the systems. For this purpose we use the metacat data catalog to describe the data and collections and the rucio file storage system to determine where replicas of files are and provide a url that allows you to process them. There is also a legacy SAM data access system that can be used for older files.
There are currently > 27M files cataloged in metacat with a total size of > 48 PB.
Key idea:
metacattells us what the file is and how it was made, with what software.ruciotells us where the file is, and gets it and keeps it where it is supposed to be.
All rucio entries should have a metacat entry describing them. With a few exceptions (retired, intermediate files), metacat entries correspond to real files in rucio.
How do I use this.
If you want to access data, this module will help you find and examine it.
If you want to process data using the full power of DUNE computing, you should talk to the data management group about methods for cataloging any data files you plan to produce. This will allow you to use DUNE’s collaborative storage capabilities to preserve and share your work with others and will be required for publication of results.
How to find and access official data
Official datasets
The production group make official datasets which are sets of files which share important characteristics such as experiment, data_tier, data_stream, processing version and processing configuration. Often all you need is an official dataset.
See DUNE Physics Datasets for a detailed description.
Fast web catalog queries
You can do fast string queries based on keywords embedded in the dataset name.
Go to dunecatalog and log in with your services password.
Choose your apparatus (Far Detector for example), use the category key to further refine your search and then type in keywords. Here I chose the Far Detectors tab and the FD-VD category from the pulldown menu.
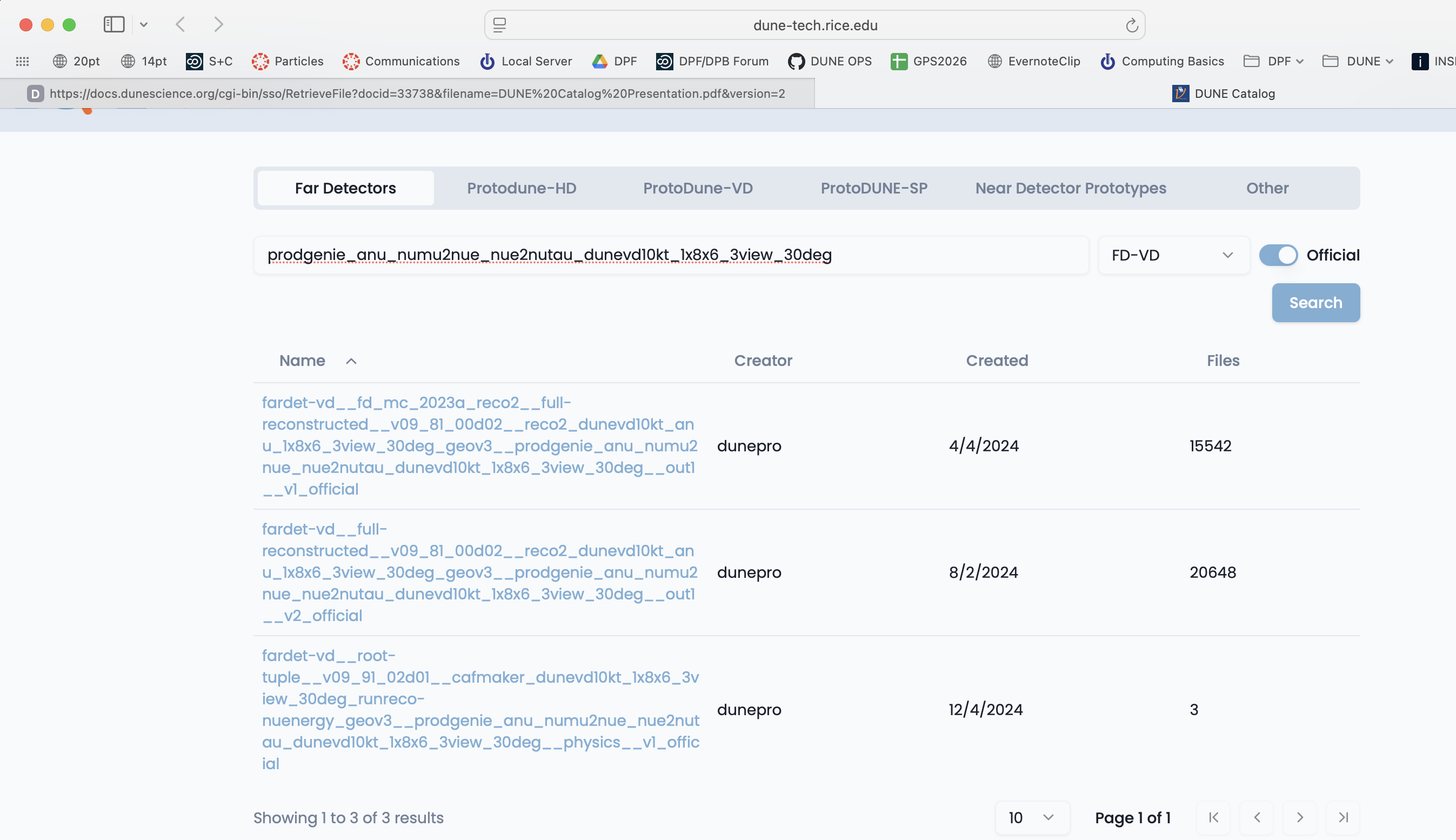
If you click on a dataset you can see a sample of the files inside it.
You can find a more detailed tutorial for the dunecatalog site at: Dune Catalog Tutorial
Command line tools and advanced queries
You can also explore and find the right dataset on the command line by using metacat dataset keys:
First you need to know your namespace and then explore within it.
metacat namespace list # find likely namespaces
There are official looking ones like hd-protodune-det-reco and ones for users doing production testing like schellma. The default for general use is usertests
Creation of namespaces by non-privileged users is currently disabled. A tool is in progress which will automatically make one namespace for each user
metacat web interface
Metacat also has a web interface that is useful in exploring file parentage metacat gui
Example of finding reconstructed Monte Carlo
Let’s look for some reconstructed Monte Carlo from the VD far detector.
metacat query "datasets matching fardet-vd:*official having core.data_tier=full-reconstructed"
Lots of output … looks like there are 2 types of official ones - let’s get “v2”
metacat query "datasets matching fardet-vd:*v2_official having core.data_tier=full-reconstructed"
and there are then several different generators. Let’s explore reconstructed simulation of the vertical drift far detector.
metacat query "datasets matching fardet-vd:*v2_official having core.data_tier=full-reconstructed and dune_mc.gen_fcl_filename=prodgenie_nu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg.fcl"
Ok, found the official neutrino beam dataset:
fardet-vd:fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_nu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_nu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official
metacat query "datasets matching fardet-vd:*v2_official having core.data_tier=full-reconstructed and dune_mc.gen_fcl_filename=prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg.fcl"
And the anti-neutrino dataset:
fardet-vd:fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official
you can use the web data catalog to do advanced searches
You can also do keyword/value queries like the ones above using the Other tab on the web-based Data Catalog.
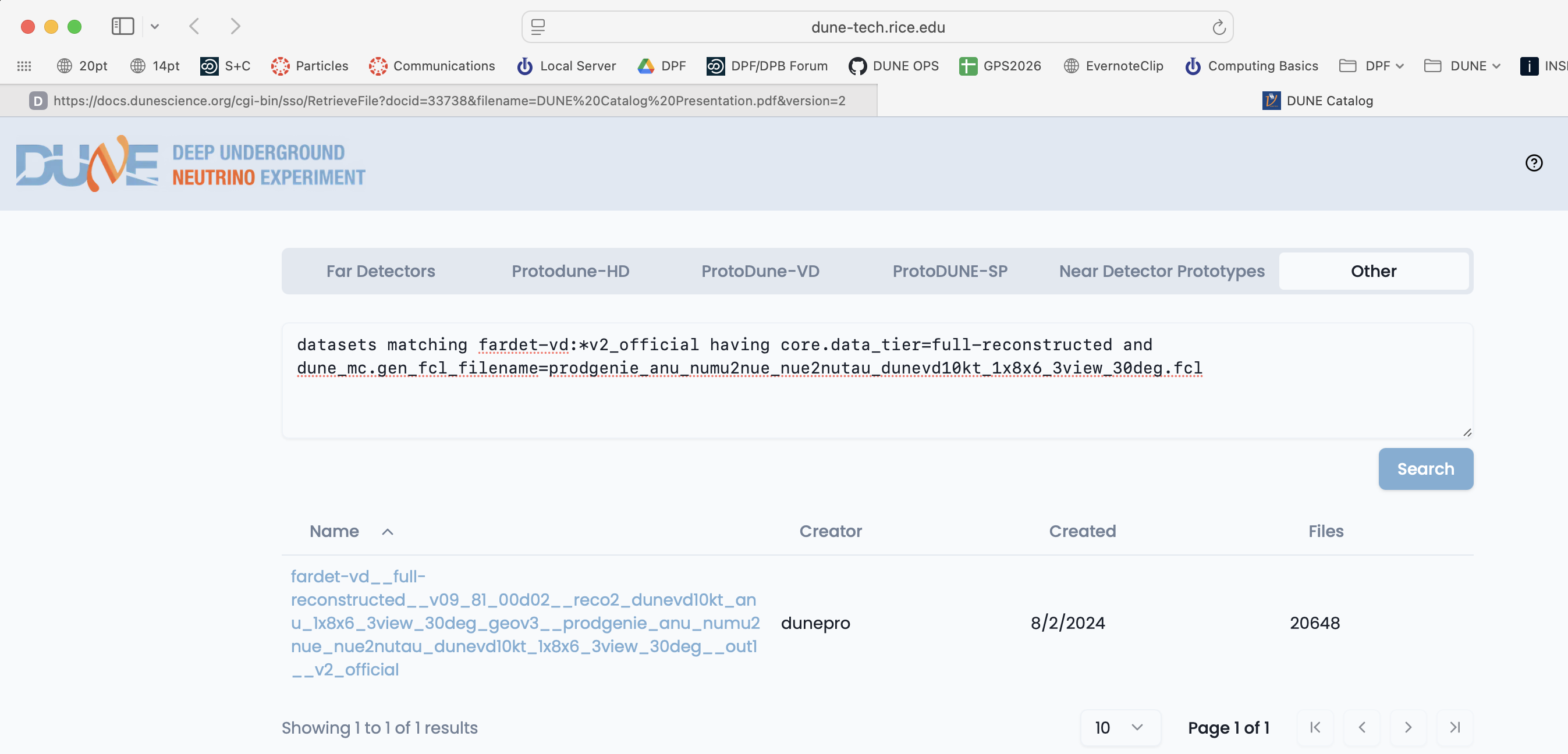
You can also query the catalogs yourself using metacat and rucio catalogs. Metacat contains information about file content and official datasets, rucio stores the physical location of those files. Files should have entries in both catalogs. Generally you ask metacat first to find the files you want and then ask rucio for their location.
What is metacat?
Metacat is a file and dataset catalog - it allows you to search for files and datasets that have particular attributes and understand their provenance, including details on all of their processing steps. It also allows for querying jointly the file catalog and the DUNE conditions database.
You can find extensive documentation on metacat at:
Find a file in metacat
DUNE runs multiple experiments (far detectors, protodune-sp, protodune-dp hd-protodune, vd-protodune, iceberg, coldboxes… ) and produces various kinds of data (mc/detector) and process them through different phases.
To find your data you need to specify at the minimum
core.run_type(the experiment: fardet-vd, hd-protodune …)core.file_type(mc or detector)core.data_tier(the level of processing raw, full-reconstructed, root-tuple …)
and when searching for specific types of data
core.data_stream(physics, calibration, cosmics)core.runs[any]=<runnumber>
For processed data you also need to know about
core.application.version(version of code run)dune.config_file(configuration file for the reconstruction/simulation)dune_mc.gen_fcl_filename(configuration for the initial simulation physics)dune.output_status(This should be ‘confirmed’ for processed files. If it is not, the file likely never got stored.)core.data_tier(what kind of output is it?)
Example of doing a metacat search
Here is an example of a metacat query that gets you raw files from a recent ‘hd-protodune’ cosmics run.
Note: there are example setups that do a full setup in the extras folder:
First get metacat if you have not already done so
SL7
Make certain you have dune software set up SL7 setup
AL9
Make certain you have AL9 set up AL9 setup
then do queries to find particular groups of files
metacat query "files from dune:all where core.file_type=detector and core.run_type=hd-protodune and core.data_tier=raw and core.runs[any]=27331 ordered limit 1"
this should give you a file:
hd-protodune:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408.hdf5
the string before the ‘:’ is the namespace and the string after is the filename.
You can find out more about your file by doing:
metacat file show -m -l hd-protodune:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408.hdf5
which gives you a lot of information:
checksums:
adler32 : 5222f2ae
created_timestamp : 2024-06-20 17:38:45.141418+00:00
creator : dunepro
fid : 83316551
name : np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408.hdf5
namespace : hd-protodune
size : 4238541524
updated_timestamp : 1718905125.141418
metadata:
core.data_stream : physics
core.data_tier : raw
core.end_time : 1718904863.0
core.event_count : 35
core.events : [35564, 35568, 35572, 35576, 35580, 35584, 35588, 35592, 35596, 35600, 35604, 35608, 35612, 35616, 35620, 35624, 35628, 35632, 35636, 35640, 35644, 35648, 35652, 35656, 35660, 35664, 35668, 35672, 35676, 35680, 35684, 35688, 35692, 35696, 35700]
core.file_content_status: good
core.file_format : hdf5
core.file_type : detector
core.first_event_number: 35564
core.last_event_number: 35700
core.run_type : hd-protodune
core.runs : [27331]
core.runs_subruns : [2733100001]
core.start_time : 1718904848.0
dune.daq_test : False
retention.class : physics
retention.status : active
children:
hd-protodune-det-reco:np04hd_run27331_calibana_merged_1.root (cl7b7XQpTpS3PGm5)
hd-protodune-det-reco:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408_reco_stage1_reco_stage2_20240926T225231_keepup_hists.root (Kf6CttcJRJu2uk58)
hd-protodune-det-reco:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408_reco_stage1_reco_stage2_20240926T225231_keepup.root (sxh5FHKLTGym6pDp)
hd-protodune-det-reco:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408_reco_stage1_reco_stage2_20240623T013207_keepup.root (Xl9QXEo0RouAqO0s)
hd-protodune-det-reco:np04hd_raw_run027331_0254_dataflow0_datawriter_0_20240620T173408_reco_stage1_20240623T013207_keepup_hists.root (xWIH9tmnSWqWBJE5)
What do those fields mean?
look in the glossary to see what those fields mean.
Warning - there are multiple child files that look similar
Files can be reprocessed with different versions and can be reprocessesd twice if the batch system gets confused. Experts can tell them apart with specific queries about reconstruction versions and file status (in this case there were 2 reconstruction versions core.application.version = v09_90_02d00 and v09_91_02d01).
If you are doing real analysis please use the official datasets which experts have defined
if no official dataset exists, you need to require additional fields like:
dune.output_status=confirmedandcore.application.version=v09_91_02d01anddune.config_file=standard_reco_stage2_calibration_protodunehd_keepup.fclto make certain that the job that created the file actually wrote the output back to storage and you are not looking at 2 versions of the same file.
find out how much raw data there is in a run using the summary option
metacat query -s "files from dune:all where core.file_type=detector \
and core.run_type=hd-protodune and core.data_tier=raw \
and core.data_stream=physics and core.runs[any]=27331"
Files: 4144
Total size: 17553648200600 (17.554 TB)
get a limited number of files in a query
Batch workflows with more than 10,000 files are strongly discouraged (largely as when they fail, they fail BIG!). You can chop up larger sets by using the skip and limit fields in your query.
To chop up a big query into smaller chunks:
export MYBIGQUERY=<your query>
export MYQUERY1="$MYBIGQUERY ordered skip 0 limit 1000"
export MYQUERY2="$MYBIGQUERY ordered skip 1000 limit 1000"
export MYQUERY3="$MYBIGQUERY ordered skip 2000 limit 1000"
..etc.
-
the
orderedassures that your query is reproducible -
the
skipneeds to appear before thelimit
Always look at the output of your workflow on one of the queries before submitting them all.
find out how much data there is in a dataset
Do a query of a dataset using the -s or --summary option
metacat query -s "files from fardet-vd:fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official"
Files: 20648
Total size: 34550167782531 (34.550 TB)
this may take a while as that is a big dataset.
What describes a dataset?
Let’s look at the metadata describing an anti-neutrino dataset: the -j means json output
metacat dataset show -j fardet-vd:fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official
{
"created_timestamp": 1722620726.662696,
"creator": "dunepro",
"description": "files where namespace='fardet-vd' and core.application.version=v09_81_00d02 and core.application.name=reco2 and core.data_stream=out1 and core.data_tier='full-reconstructed' and core.file_type=mc and core.run_type='fardet-vd' and dune.campaign=fd_mc_2023a_reco2 and dune.config_file=reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3.fcl and dune.requestid=ritm1780305 and dune_mc.detector_type='fardet-vd' and dune_mc.gen_fcl_filename=prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg.fcl and dune.output_status=confirmed and core.group=dune",
"file_count": 20648,
"file_meta_requirements": {},
"frozen": true,
"metadata": {
"core.application.name": "reco2",
"core.application.version": "v09_81_00d02",
"core.data_stream": "out1",
"core.data_tier": "full-reconstructed",
"core.file_type": "mc",
"core.group": "dune",
"core.run_type": "fardet-vd",
"datasetpar.deftag": "v2_official",
"datasetpar.max_time": null,
"datasetpar.min_time": null,
"datasetpar.namespace": "fardet-vd",
"dune.campaign": "fd_mc_2023a_reco2",
"dune.config_file": "reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3.fcl",
"dune.output_status": "confirmed",
"dune.requestid": "ritm1780305",
"dune_mc.detector_type": "fardet-vd",
"dune_mc.gen_fcl_filename": "prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg.fcl"
},
"monotonic": false,
"name": "fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official",
"namespace": "fardet-vd",
"updated_by": null,
"updated_timestamp": null
}
You can use any of those keys to refine dataset searches as we did above. You probably have to ask your physics group which are interesting.
What files are in that dataset and how do I use them?
You can either locate and click on a dataset in the web data catalog or use themetacat web interface or use the command line:
metacat query "files from fardet-vd:fardet-vd__full-reconstructed__v09_81_00d02__reco2_dunevd10kt_anu_1x8x6_3view_30deg_geov3__prodgenie_anu_numu2nue_nue2nutau_dunevd10kt_1x8x6_3view_30deg__out1__v2_official ordered limit 10"
will list the first 10 files in that dataset (you probably don’t want to list all 20648)
You can also use a similar query in your batch job to get the files you want.
Finding those files on disk
To find your files, you need to use Rucio directly or give the justIN batch system your query and it will locate them for you.
Getting file locations using Rucio
What is Rucio?
Rucio is the next-generation Data Replica service and is part of DUNE’s new Distributed Data Management (DDM) system that is currently in deployment. Rucio has two functions:
- A rule-based system to get files to Rucio Storage Elements around the world and keep them there.
- To return the “nearest” replica of any data file for use either in interactive or batch file use. It is expected that most DUNE users will not be regularly using direct Rucio commands, but other wrapper scripts that calls them indirectly.
As of the date of the 2025 tutorial:
- The Rucio client is available in CVMFS and Spack
- Most DUNE users are now enabled to use it. New users may not automatically be added.
You will need to authenticate to read files
For SL7 use justin to get a token
Interactive file access
To get a token that allows you to access files interactively in SL7
htgettoken -i dune --vaultserver htvaultprod.fnal.gov -r interactive
export BEARER_TOKEN_FILE=/run/user/`id -u`/bt_u`id -u`
export X509_CERT_DIR=/cvmfs/oasis.opensciencegrid.org/mis/certificates
put this in a file called dune_token.sh
The first time you do this you will see:
Attempting kerberos auth with https://htvaultprod.fnal.gov:8200 ... succeeded
Attempting to get token from https://htvaultprod.fnal.gov:8200 ... failed
Attempting OIDC authentication with https://htvaultprod.fnal.gov:8200
Complete the authentication at:
https://cilogon.org/device/?user_code=XXXX
No web open command defined, please copy/paste the above to any web browser
Waiting for response in web browser
Go to that web site and authenticate
Storing vault token in /tmp/vt_uXXX
Saving credkey to /nashome/s/USER/.config/htgettoken/credkey-dune-interactive
Saving refresh token ... done
Attempting to get token from https://htvaultprod.fnal.gov:8200 ... succeeded
Storing bearer token in /run/user/XXXX/bt_XXXX
Accessing rucio and justIn resources requires a bit more
in SL7 - put this in a file called dune_data_sl7.sh so you can use it again.
setup metacat
setup rucio
export RUCIO_ACCOUNT=justinreadonly
setup justin
justin time # this just tells justin that you exist and want to authenticate
justin get-token # this actually gets a token and associated proxy for access to rucio and the batch system
The first time you do this you will get asked (after the justin time command)
To authorize this computer to run the justin command, visit this page with your
usual web browser and follow the instructions within the next 10 minutes:
https://dunejustin.fnal.gov/authorize/XXXXX
Check that the Session ID displayed on that page is BfhVBmQ
Once you've followed the instructions on that web page, please run the command
you tried again. You won't need to authorize this computer again for 7 days.
Once again go to the website that appears and authenticate. After the first authentication to justIn you need to do a second justin call
justin get-token
You will need to do this sequence weekly as your justin access expires.
Note:
Despite the name of this command it gets you both a token and a special X.509 proxy and it is the latter you are actually using to talk to rucio in these SL7 examples
for AL9 use htgettoken to get a token
Interactive file access
Make certain you have al9 set up
Then use htgettoken to get a token so you can read the files you find.
htgettoken -i dune --vaultserver htvaultprod.fnal.gov -r interactive
export BEARER_TOKEN_FILE=/run/user/`id -u`/bt_u`id -u`
The first time you do it it will ask you to authenticate using a web browser.
You should be able to read files at remote sites now.
You may need to repeat the htgettoken as the interactive tokens are pretty short-lived. Batch jobs do their own tokens.
Accessing rucio and justIn resources requires a bit more
You should already be set up above. Now you can use justIn to get you a token.
- First tell
justInknows about you
justin time
The first time you do this you will get asked (after the justin time command)
To authorize this computer to run the justin command, visit this page with your
usual web browser and follow the instructions within the next 10 minutes:
https://dunejustin.fnal.gov/authorize/XXXXX
Check that the Session ID displayed on that page is BfhVBmQ
Once you've followed the instructions on that web page, please run the command
you tried again. You won't need to authorize this computer again for 7 days.
Once again go to the website that appears and authenticate.
- After the first authentication to justIn you need to do a second justin call
justin get-token
You will need to do this sequence weekly as your justin access expires.
Note:
Despite the name of this command it gets you both a token and a special X.509 proxy and it is the latter you are actually using to talk to rucio in these SL7 examples
finding a file
Then use rucio to find out about a file’s locations. the –protocols flag makes certain you get the streaming root: location.
rucio replica list file fardet-vd:prodmarley_nue_es_flat_radiological_decay0_dunevd10kt_1x8x14_3view_30deg_20250217T033222Z_gen_004122_supernova_g4stage1_g4stage2_detsim_reco.root --pfns --protocols=root
returns 2 locations:
root://fndca1.fnal.gov:1094/pnfs/fnal.gov/usr/dune/tape_backed/dunepro//fardet-vd/hit-reconstructed/2025/mc/out1/le_mc_2024a/00/00/51/85/prodmarley_nue_es_flat_radiological_decay0_dunevd10kt_1x8x14_3view_30deg_20250217T033222Z_gen_004122_supernova_g4stage1_g4stage2_detsim_reco.root
root://meitner.tier2.hep.manchester.ac.uk:1094//cephfs/experiments/dune/RSE/fardet-vd/fd/a6/prodmarley_nue_es_flat_radiological_decay0_dunevd10kt_1x8x14_3view_30deg_20250217T033222Z_gen_004122_supernova_g4stage1_g4stage2_detsim_reco.root
which the locations of the file on disk and tape. We can use this to copy the file to our local disk or access the file via xroot.
Testing - access a file
Try to access the file at manchester using the command:
root -l root://meitner.tier2.hep.manchester.ac.uk:1094//cephfs/experiments/dune/RSE/fardet-vd/fd/a6/prodmarley_nue_es_flat_radiological_decay0_dunevd10kt_1x8x14_3view_30deg_20250217T033222Z_gen_004122_supernova_g4stage1_g4stage2_detsim_reco.root _file0->ls()
It will complain because you haven’t loaded all the information needed to read an artroot file but you should be able to read it.
NOTE if you see a path in
/pnfs/usr/dune/tape_backedat Fermilab or oneosctapublic.cern.chthose are on tape and not generally accessible to the user. Try to get the file from the remaining one (in this case hep.manchester.ac.uk)
More finding files by characteristics using metacat
There isn’t always an official dataset so you can also list files directly using metacat.
To list raw data files for a given run:
metacat query "files where core.file_type=detector \
and core.run_type='protodune-sp' and core.data_tier=raw \
and core.data_stream=physics and core.runs[any] in (5141)"
core.run_typetells you which of the many DAQ’s this came from.core.file_typetells detector from mccore.data_tiercould be raw, full-reconstructed, root-tuple. Same data different formats.
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0013_dl7.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0005_dl3.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0003_dl1.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0004_dl7.root
...
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0009_dl7.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0014_dl11.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0007_dl6.root
protodune-sp:np04_raw_run005141_0011_dl8.root
Note the presence of both a namespace and a filename
What about some files from a reconstructed version?
metacat query "files from dune:all where core.file_type=detector \
and core.run_type='protodune-sp' and core.data_tier=full-reconstructed \
and core.data_stream=physics and core.runs[any] in (5141) and dune.campaign=PDSPProd4 ordered limit 10"
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0013_dl10_reco1_18127013_0_20210318T104043Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0015_dl4_reco1_18126145_0_20210318T101646Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0008_dl12_reco1_18127279_0_20210318T104635Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0002_dl2_reco1_18126921_0_20210318T103516Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0002_dl14_reco1_18126686_0_20210318T102955Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0015_dl5_reco1_18126081_0_20210318T122619Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0017_dl10_reco1_18126384_0_20210318T102231Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0006_dl4_reco1_18127317_0_20210318T104702Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0007_dl9_reco1_18126730_0_20210318T102939Z.root
pdsp_det_reco:np04_raw_run005141_0011_dl7_reco1_18127369_0_20210318T104844Z.root
To see the total number (and size) of files that match a certain query expression, then add the -s option to metacat query.
See the metacat documentation for more information about queries. DataCatalogDocs and check out the glossary of common fields at: MetaCatGlossary
Accessing data for use in your analysis
To access data without copying it, XRootD is the tool to use. However it will work only if the file is staged to the disk.
You can stream files worldwide if you have a DUNE VO certificate as described in the preparation part of this tutorial.
To learn more about using Rucio and Metacat to run over large data samples go here:
Full justIN/Rucio/Metacat Tutorial
Exercise 1
- Use
metacat query ....to find a file from a particular experiment/run/processing stage. Look in DataCatalogDocs for hints on constructing queries.- Use
metacat file show -m -l namespace:filenameto get metadata for this file. Note that--jsongives the output in json format.
When we are analyzing large numbers of files in a group of batch jobs, we use a metacat dataset to describe the full set of files that we are going to analyze and use the JustIn system to run over that dataset. Each job will then come up and ask metacat and rucio to give it the next file in the list. It will try to find the nearest copy. For instance if you are running at CERN and analyzing this file it will automatically take it from the CERN storage space EOS.
Exercise 2 - explore in the gui
The Metacat Gui is a nice place to explore the data we have.
You need to log in with your services (not kerberos) password.
do a datasets search of all namespaces for the word official in a dataset name
you can then click on sets to see what they contain
Exercise 3 - explore a dataset
Use metacat to find information about the dataset justin-tutorial:justin-tutorial-2024 How many files are in it, what is the total size. (metacat dataset show command, and metacat dataset files command) Use rucio to find one of the files in it.
Resources:
Quiz
Question 01
What is file metadata?
- Information about how and when a file was made
- Information about what type of data the file contains
- Conditions such as liquid argon temperature while the file was being written
- Both A and B
- All of the above
Answer
The correct answer is D - Both A and B.
Comment here
Question 02
How do we determine a DUNE data file location?
- Do `ls -R` on /pnfs/dune and grep
- Use `rucio replica list file` (namespace:filename) --pnfs --protocols=root
- Ask the data management group
- None of the Above
Answer
The correct answer is B - use
rucio replica list file(namespace:filename).Comment here
Useful links to bookmark
- DataCatalog: https://dune.github.io/DataCatalogDocs
- metacat: [https://dune.github.io/DataCatalogDocs/]
- rucio: [https://rucio.github.io/documentation/]
- Pre-2024 Official dataset definitions: dune-data.fnal.gov
- UPS reference manual
- UPS documentation (redmine)
- UPS qualifiers: About Qualifiers (redmine)
- mrb reference guide (redmine)
- CVMFS on DUNE wiki: Access files in CVMFS
Key Points
SAM and Rucio are data handling systems used by the DUNE collaboration to retrieve data.
Staging is a necessary step to make sure files are on disk in dCache (as opposed to only on tape).
Xrootd allows user to stream data files.